Google Tag Manager is a revolutionary tool for devising and using tracking codes on any website or application’s deployment. In brief, in this article, I’ll describe how GTM is helping in achieving their end goals-efficient tracking via optimization campaigns with actionable insights from a single point of view.
What are Google Tags?
Google Tags are snippets of code or tracking scripts used to collect and send data about user interactions on your website or app to analytics and marketing platforms. These tags help measure website performance, track user behavior, and optimize campaigns.
What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager (GTM) is a completely free tag manager system by Google, makes it easier to manage and deploy tracking tags, analytics scripts, or any other javascript code directly on your website or app by editing the underlying code rather than doing it in an indirect method. It works as a channel through which you can add, modify, or control all these tags using a user-friendly interface.
GTM tags are small pieces of code that are used to collect data about user behavior like page views, events, or interactions, which can be used later to improve the performance of marketing campaigns or track the performance of a website. Instead of changing each time code of your website, with GTM, one can make changes between its features and thus saves time and avoids errors.
This tool is brilliant for marketers and developers as well, as it has a user-friendly interface and requires little knowledge in coding but can help in getting accurate tracking of user’s activities in the websites or apps.
How Does Google Tag Manager Work?
Google Tag Manager operates through three core components: Tags, triggers, and variables, which work together to enable efficient tracking and data collection.
Tags
Tags are pieces of code or scripts that perform specific tasks, such as tracking user actions or collecting data. Instead of adding these scripts directly to your website, you create and configure them in GTM.
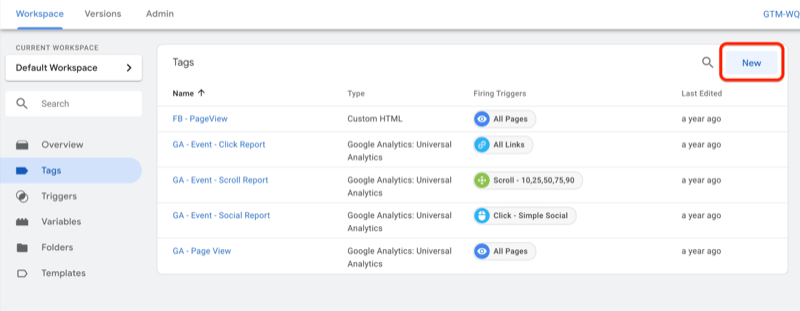
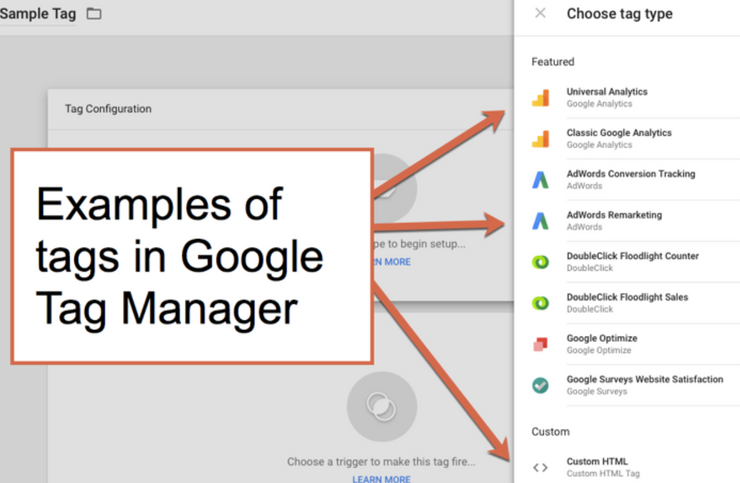
Google Tag Manager examples of Tags:
- Google Analytics for tracking page views.
- Facebook Pixel for conversion tracking and remarketing.
- Hotjar or Crazy Egg for heatmaps and user behavior analysis.
How It Works: Tags are created within GTM and assigned specific rules (via triggers) for when they should activate. This eliminates the need to hard-code tags into your website repeatedly.
Triggers
Triggers define the conditions under which a tag will execute. They answer the question, “When should this tag fire?”
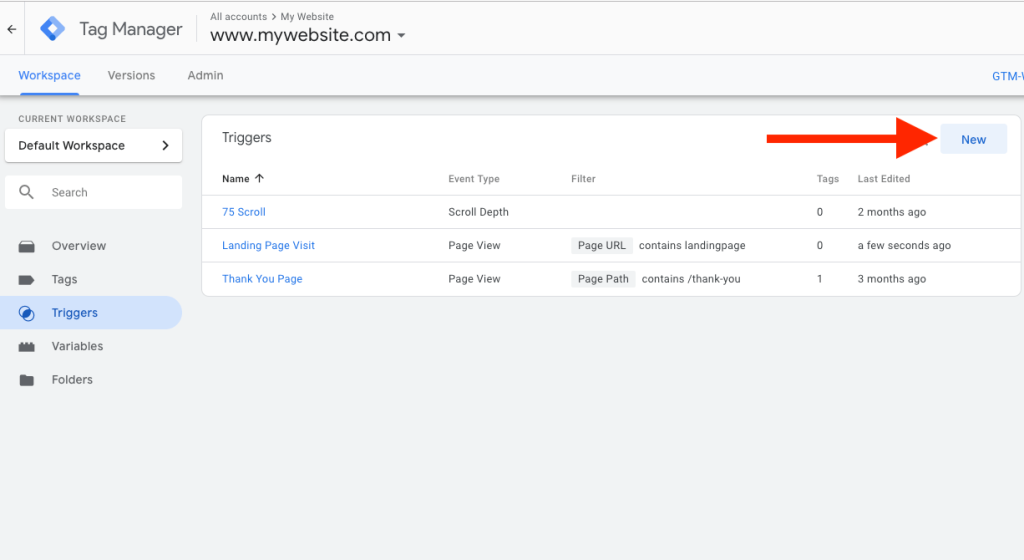
Google Tag Manager examples of Trigger Types:
- Pageview trigger fires when a user lands on a specific page.
- Click trigger activates when a button, link, or other clickable element is clicked.
- Form submission trigger fires when a user submits a form.
- Custom event trigger listens for specific JavaScript-based actions, such as scrolling or interactions.
How It Works: You set conditions (e.g., “URL contains ‘checkout’”) for the trigger. When those conditions are met, the associated tag is activated. This allows precise control over when and where tracking occurs.
Variables
Variables provide dynamic values that tags and triggers can use to perform their tasks. They act as placeholders that adapt based on user behavior or page context.

Google Tag Manager examples of Variables:
- Built-in variables include common options like Page URL, Click Text, or Referrer.
- Custom variables allow you to capture specific data, like product IDs or form inputs.
How It Works:
Tags and triggers rely on variables to define what data to collect or evaluate.
For example, a trigger might fire only when the variable “Page Path” equals “/thank-you.” Similarly, a tag could send a custom event to Google Analytics using the value of a variable like “Form Submission ID.”
What is Google Tag Manager Used For?
Why use Google Tag Manager? Google Tag Manager (GTM) helps streamline tracking and analytics by managing tags and integrating various tools in one platform. Here are its key uses:
- Managing Tags: Centralizes all tracking scripts like Google Analytics or Facebook Pixel.
- Tracking User Actions: Monitors events such as clicks, form submissions, or scroll depth.
- Tool Integration: Works seamlessly with marketing and analytics platforms like Google Ads or Hotjar.
- Debugging Tags: Tests and ensures tags fire correctly before going live.
- Simplifying Updates: Allows marketers to make quick changes without developer support.
Benefits of Using Google Tag Manager?
1. Simplified Tag Management
GTM removes the tedious process of hard-coding single tags in your site, which serves as a one-stop portal to add, manage and exclude tags. You won’t need to visit your website’s code for every new tracking mechanism or update, but you can do all that from GTM.
All this makes deployment way faster and massively lowers risk of errors in coding which could jam your entire site.
2. Empowering Non-Developers
GTM is a platform where marketers and analysts can take charge of tracking without requiring extensive coding experience or a developer’s assistance. The platform offers an easy interface by which users can create tags, set triggers, and determine variables using little technical know-how.
Such independence ensures that marketing campaigns and analytics tracking are rolled out faster.
3. Centralized Tracking and Management
GTM is where all tags, triggers, and variables can be found under one roof: your single-source location for managing everything from setting up for tracking. You will find it easier to organize, maintain, and update tracking scripts across your website or app.
For those businesses with more complex tracking needs, this offers a standardization and, thus, lowers the chances for error and missing scripts.
4. Testing and Debugging Tools
GTM also offers a built-in Preview Mode where users can test and debug tags before going to production. This means the user can be sure that the tags will fire properly within the established parameters, allowing them to address issues prior to going live.
Troubleshooting in a controlled environment significantly reduces the chance of broken or incorrect tracking on your site.
5. Integration of Google and Third Party Tools
This is the perfect integration of Google Analytics, Google Ads, and other Google services, which makes GTM a great tool for powerful digital marketing in itself.

Google Tag Manager vs. Google Analytics
Google Tag Manager (GTM) and Google Analytics (GA) are complementary tools used for tracking and analyzing website or app data, but they serve different purposes. Here’s a comparison to clarify their roles:
| Feature | Google Tag Manager (GTM) | Google Analytics (GA) |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | A tag management system to deploy and manage tracking scripts and tags. | A data analysis tool to collect, process, and report user behavior and website performance. |
| Functionality | Deploys tags, manages triggers, and variables for tracking tools. | Tracks metrics like sessions, bounce rates, and conversions; provides insights into traffic sources and behavior. |
| Role in Tracking | Acts as the middleman for deploying tracking codes like Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, or custom scripts. | Processes data collected by tracking tags and generates reports for analysis. |
| Data Processing | Does not process or store data itself; facilitates tag execution. | Processes and stores data collected by tracking scripts for analysis and reporting. |
| User Control | Allows marketers and analysts to update tags without involving developers. | Provides data insights for analysts to optimize marketing and user experience. |
| Integration | Integrates with multiple tools like Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, LinkedIn Insight Tag, and Hotjar. | Integrates with GTM, Google Ads, and other Google tools for comprehensive reporting and optimization. |
| Key Focus | Simplifying the deployment and management of tracking tags. | Providing actionable insights by analyzing website and user behavior data. |
| Best For | Marketers and businesses managing multiple tracking tools or needing flexibility with tag updates. | Analysts and marketers needing to interpret user behavior and website performance data. |
From the table above, we can conclude that Google Tag Manager (GTM) is best for managing and deploying multiple tracking tags efficiently without editing code, making it ideal for marketers handling frequent updates or third-party tools.
Meanwhile, Google Analytics (GA) focuses on analyzing user behavior and website performance, providing actionable insights and detailed reports.

Therefore, combining both tools offers a seamless solution for streamlined tag management and comprehensive data analysis.
Steps to Set Up Google Tag Manager
Option 1: Set up Manually
Step 1: Create a GTM Account: Sign up at Google Tag Manager, create an account, and set up a container for your website or app.
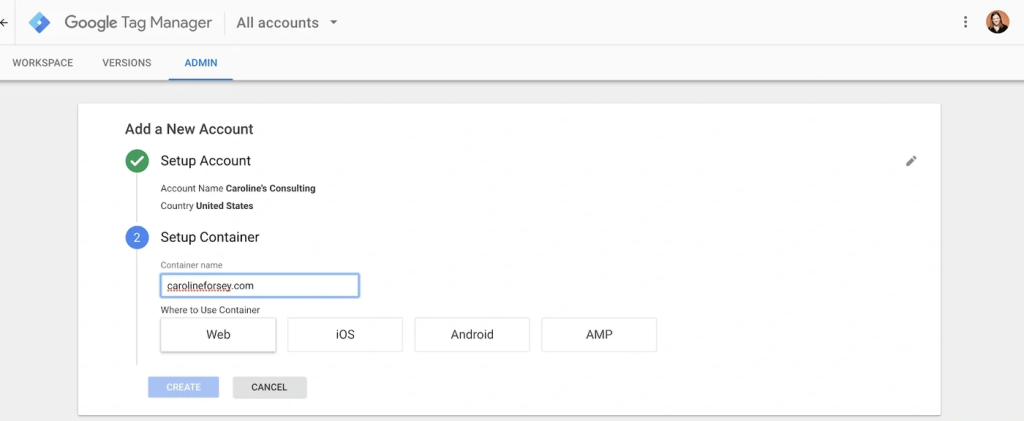
Step 2: Install GTM Code: Copy the provided code snippets and place them in the <head> and <body> sections of your website or integrate them via your CMS.
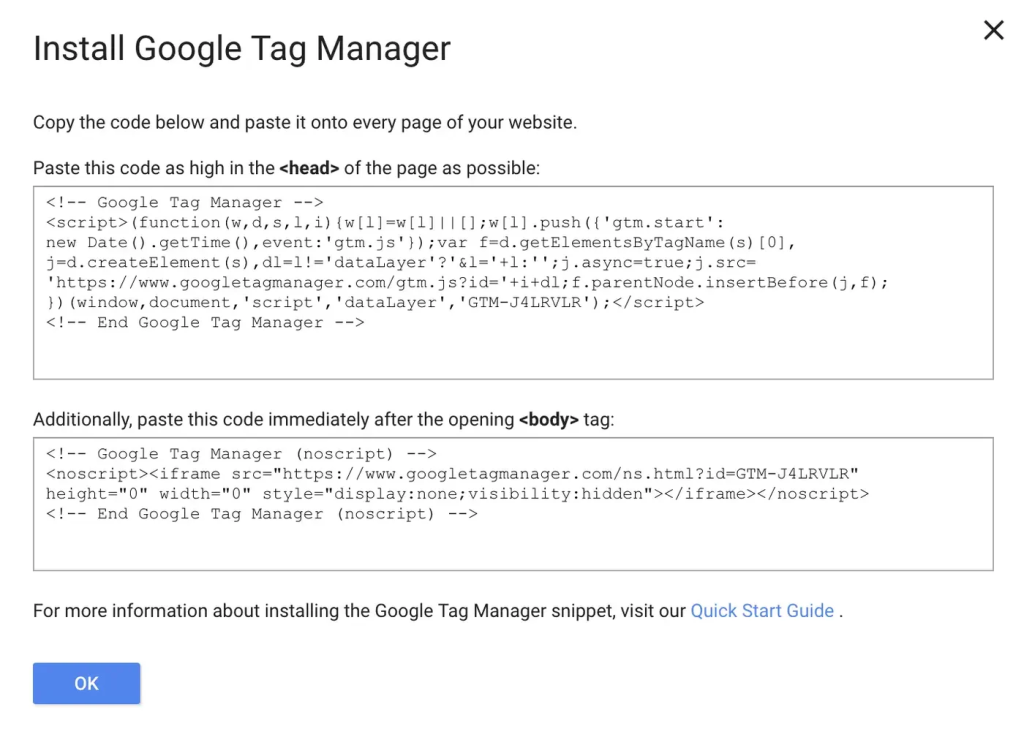
Step 3: Add Initial Tags: Start with a basic tag, such as Google Analytics, and set up triggers to define when it should fire.
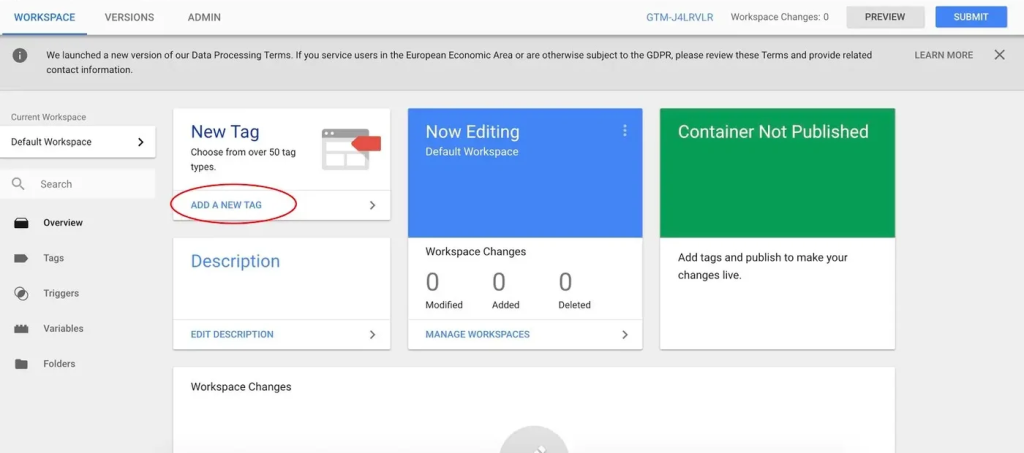
Define when tags should fire, such as on page views, button clicks, or form submissions.
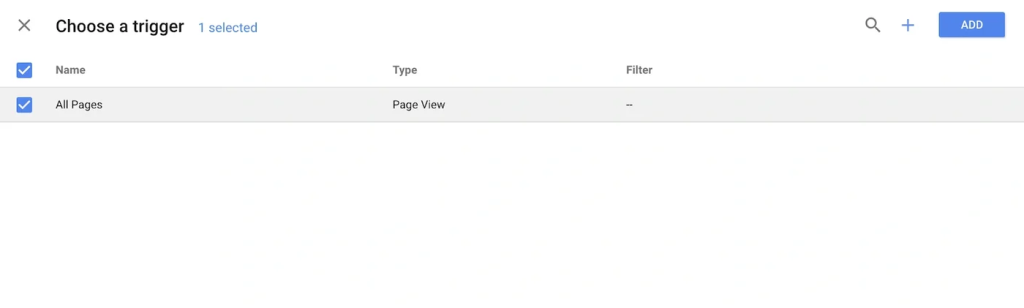
Configure variables to pass dynamic data like page URLs or event values to your tags.
With TagFly, pre-built containers simplify the process. The table below compares manual setup with using TagFly.
| Setup Task | Without TagFly (Manual Setup) | With TagFly (Using Pre-Built Containers) |
|---|---|---|
| Create Tags | Manually create tags for each event (e.g., page views, ATC). | Pre-built containers include all essential event tags. |
| Configure Triggers | Define and test triggers for each event manually. | Triggers are already configured and ready to use. |
| Set Variables | Identify and set variables for dynamic data (e.g., page paths). | Variables are pre-defined within the container. |
| Platform Integrations | Add platform-specific tags (GA4, Facebook, TikTok, etc.). | Integrations are built-in and compatible with platforms. |
| Testing and Debugging | Test each tag, trigger, and variable individually. | Containers are pre-tested for common use cases. |
| Time Investment | High: Requires detailed setup and troubleshooting. | Low: Ready-to-use containers reduce setup time. |
Step 4: Test in Preview Mode: Use the Preview Mode to ensure tags are firing correctly.
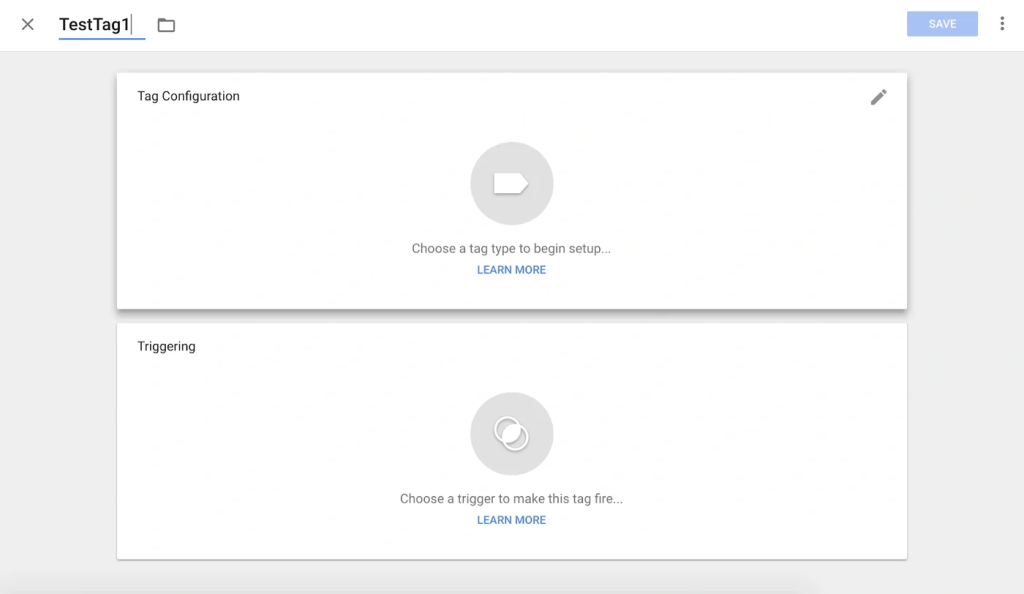
Step 5: Publish the Container: Once verified, publish the container to make it live on your website.
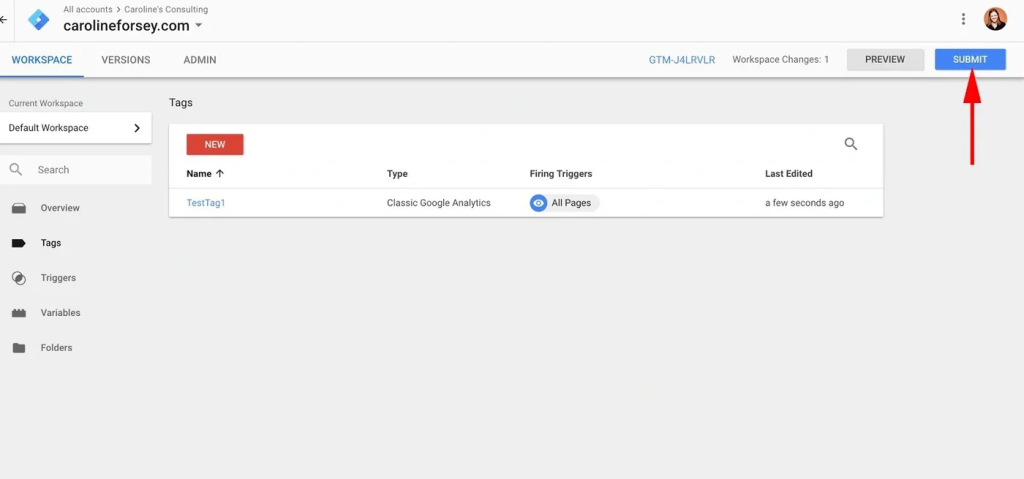
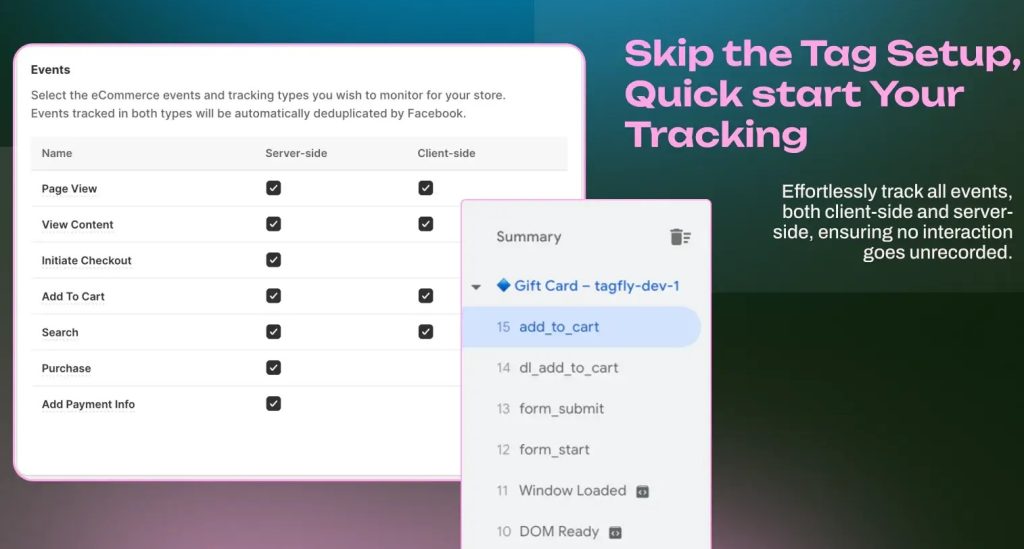
Option 2: Simplify the Setup with TagFly
With TagFly App, users can simplify the entire Google Tag Manager setup process. All they need to do is create a GTM account, and TagFly takes care of the rest. There’s no need to manually install codes or configure tags, as TagFly automatically adds the necessary tracking scripts to the user’s store.
This saves time and eliminates the complexity of traditional GTM setup, making it ideal for beginners and busy professionals.
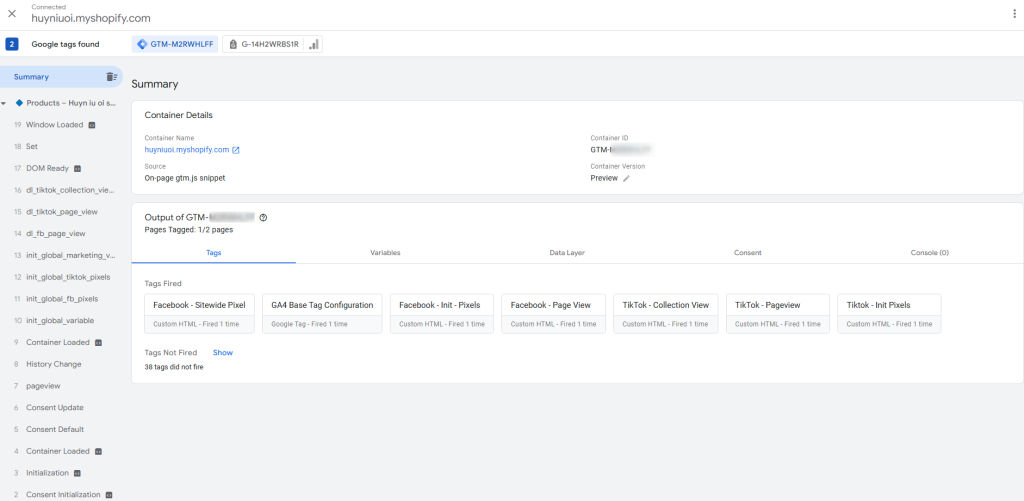
How to Verify Your Google Tag Manager Setup
Step 1: Verify Your Tag Sends Data
Open Google Tag Assistant and enter your website’s URL.
Tag Assistant will detect tags on your site. Look at the top of the interface to check if your Google Tag appears.
Step 2: Check Events in the Summary Tab
In Tag Assistant’s Summary Tab, verify if the tag is sending any events or data requests.
If the tag records and dispatches events, your setup is correct.
If the tag isn’t collecting or sending data, refer to the troubleshooting steps below.
Step 3: Ensure Your Tag is Found on All Relevant Pages
Confirm that your Google Tag is installed on every page that needs to send data.
Use the tag coverage summary in Tag Assistant to identify which pages are missing the tag.
👉 Check Google Tag Manager: How to Test & Troubleshoot in 2025
This guide provides the foundational knowledge about Google Tag Manager, perfect for beginners starting their journey with this powerful tool. Experts from Tagfly recommend taking what you’ve learned here and applying it step by step—set up your GTM account, create basic tags, and test them in Preview Mode.
Google Tag Manager simplifies tracking with tags, triggers, and variables, but tools like TagFly take it a step further. TagFly provides pre-built containers for common events like page views, add to cart, and view content, and integrates with platforms like GA4, Facebook, TikTok, and Twitter. This allows you to track multiple events effortlessly without manually setting up each tag, trigger, or variable, saving time and streamlining your workflow.
Google Tag Manager FAQs
Whether you’re new to Google Tag Manager or looking to expand your knowledge, this FAQ section answers common questions to help you better understand and use GTM effectively.

Is Google Tag Manager Free?
Google Tag Manager is completely free of cost, given that the payment can be made in some instances where you need to use those advanced features; for example, GTM 360 is free but subscription under GA 360, which costs about $150,000 annually or $12,500 monthly, is required.
How Difficult Is Google Tag Manager to Use?
Although really, it is quite easy to manage different tags in GTM, learning it isn’t exactly an exception. But once you’ve learned the balk, this GTM tool proves to be phenomenally handy in tracking a whole lot of things. It has transformed the ways analysts and marketers contend with their tags, changing the game into something smoother and more user-friendly than ever.
However, setting up can be a bit complex and time-consuming for beginners. You can either choose to set it up manually or opt for a simpler solution like TagFly App.
How do I disable Google Tag Manager?
Follow these steps to remove Google Tag Manager from your site:
- Access your site’s code editor.
- Open the file that contains the <head> section, such as header.php.
- Locate the code snippet starting with <!– Google Tag Manager –>.
- Remove the entire snippet.
- Save the changes to the file.
Once completed, Google Tag Manager will be successfully removed from all pages of your site.
Final word
Google Tag Manager simplifies tracking, boosts efficiency, and empowers you to manage tags without relying on developers. It allows one to handle tags without involving developers. It is an effective way of managing a campaign, tracking users, and drawing insights from their activities.
Hopefully, this guide can get you started and help you maximize the use of GTM for your website’s success.