As tracking and privacy rules evolve, the debate around client side vs server side has become one of the most talked-about topics in digital marketing. Choosing the right tracking method can impact everything, from data accuracy and ad performance to compliance and user experience.
| What you’ll learn in this article: ● The core differences between client-side and server-side tracking ● How each method affects speed, accuracy, and privacy compliance ● Why more brands are switching to server-side tracking in 2025 ● Practical insights on using GTM (Google Tag Manager) for both methods |
What is Client-Side Tracking?
Client-side tracking is a method where data is collected through the user’s browser. Scripts, cookies, and tracking pixels run on the client side to capture information such as page views, clicks, form submissions, or purchases, and then send it directly to analytics or advertising platforms.
Common tools: Facebook Pixel, Google Analytics (client-side setup), TikTok Pixel, and most advertising tags rely on this method by default.
Example scenario: When a visitor clicks a product page, the browser fires a pixel event that records the pageview and sends it to Facebook or Google Analytics for reporting.
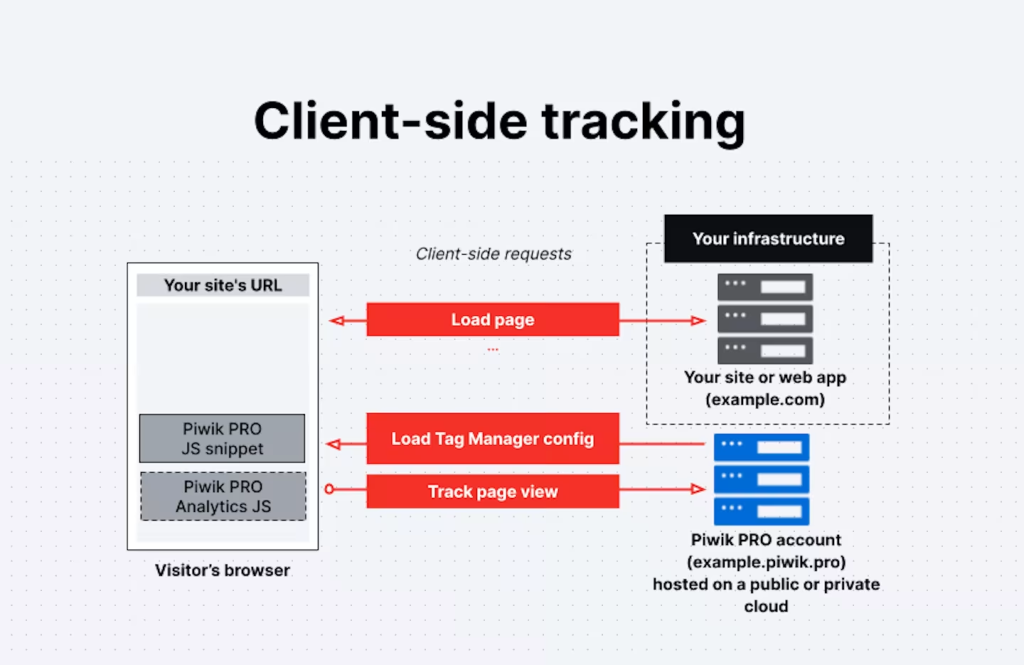
What is Server-Side Tracking?
Server-side tracking is a method where data is sent directly from the server to analytics or advertising platforms, instead of being collected through the user’s browser. The key benefit of this approach is the reduction of data loss caused by ad blockers, cookie restrictions, and browser limitations, which results in significantly more reliable and secure tracking.
Common tools: GTM Server-Side, Facebook Conversion API (CAPI), GA4 server-side.
Example scenario: When a customer makes a purchase, the backend server sends the purchase event directly to the Meta Ads API, ensuring the conversion is recorded even if the user’s browser blocks tracking scripts.
Client Side vs Server Side Tracking: Key Differences
Server side tracking vs client side tracking represent two different approaches to collecting and processing user data.
Each method has its own strengths, but in today’s privacy-first, data-driven world, server-side tracking is quickly becoming the smarter and more sustainable option for accurate, reliable insights.
1. Data Collection Point
In a client-side setup, all tracking happens inside the user’s browser, pixels and scripts capture every interaction and send data straight to analytics or ad platforms.
By contrast, server-side tracking routes those same events through your own server before forwarding them anywhere else. That middle layer gives businesses full control and ownership over what’s being shared, a major plus in the age of strict data governance.
Result:
Client-side sends data straight out; server-side lets you stay in charge of every piece of it.
2. Accuracy and Reliability
One of the biggest pain points with browser-based tracking is inconsistency. Ad blockers, privacy settings, and cookie restrictions can easily block events or cut off conversions.
With a server-side model, those roadblocks are removed entirely. Since the tracking request originates from your own server, you’re no longer at the mercy of browsers; your analytics stay accurate, stable, and complete.
Result:
Server-side ensures cleaner, more reliable data that marketers can actually trust.
3. Performance and Page Speed
Client-side scripts can pile up and slow down your website, especially if you use multiple tags.
Server-side tracking handles heavy processing in the background, freeing the browser from unnecessary work. The result is a faster, smoother experience for users and more efficient tracking for you.
Result:
Server-side boosts both performance and precision, no trade-offs required.
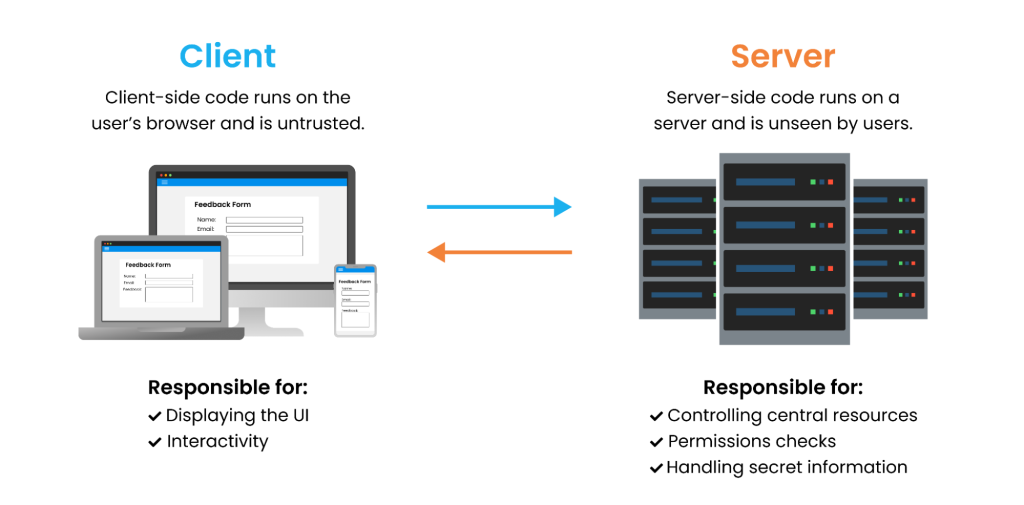
4. Privacy and Compliance
As privacy regulations evolve, client-side tracking faces more and more restrictions. Cookies expire faster, and users can easily disable or clear them.
Server-side tracking offers a more future-proof path. It lets you filter, anonymize, and protect user data before sending it anywhere, aligning your analytics with GDPR, CCPA, and ITP requirements without sacrificing insight.
Result:
Server-side is built for the privacy era, secure, transparent, and compliant by design.
5. Implementation Complexity
It’s true: setting up client-side tracking is quick and straightforward, a few lines of script, and you’re good to go. But this simplicity comes at the cost of limited flexibility and long-term control.
Server-side tracking demands a bit more initial setup, yet it’s a strategic investment. Once in place, it offers unmatched scalability, richer data control, and freedom from third-party policy changes.
Result:
Client-side is quick and easy; server-side is powerful and future-proof.
The table below gives a quick side-by-side look at how client-side and server-side tracking differ in key aspects.
| Aspect | Client-Side Tracking | Server-Side Tracking |
|---|---|---|
| Data Collection | Happens in the browser | Happens on your server |
| Accuracy | Affected by blockers & cookies | Highly accurate, reliable data flow |
| Speed | Can slow page load | Optimized performance |
| Privacy | Hard to stay GDPR-compliant | Easier privacy control |
| Setup | Easy but limited | Technical but scalable |
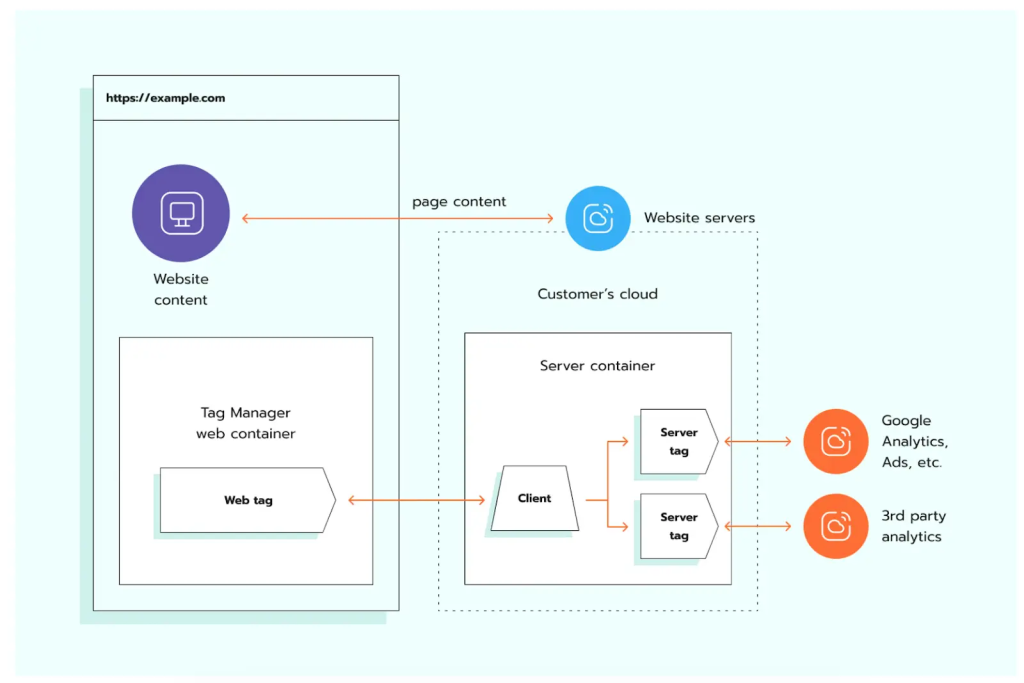
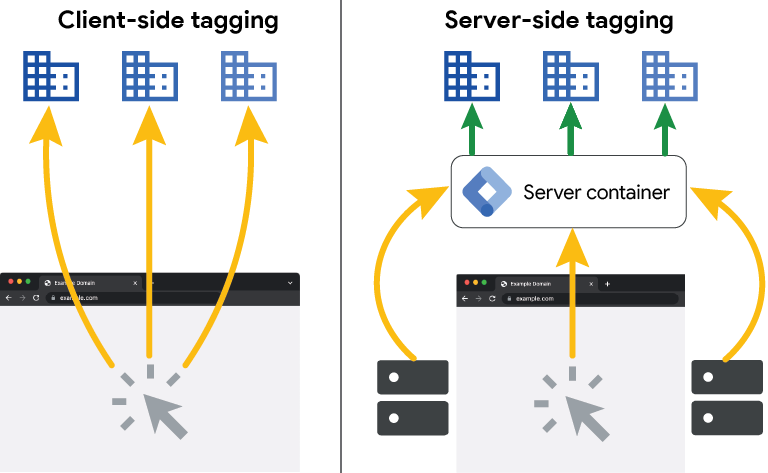
GTM Server Side vs Client Side Tagging
Specifically in Google Tag Manager (GTM), the difference between client side vs server side tracking becomes clear in how each method operates. Client-side tagging runs directly in the browser, while server-side tagging processes data through a secure cloud server for greater control and accuracy.
| Aspect | Client-Side Tagging | Server-Side Tagging |
|---|---|---|
| Setup | Uses one container placed directly on the website or app. | Uses two containers: a Web container on the site and a Server container hosted in the cloud. |
| How it works | The browser activates and sends data directly to Google or ad platforms. | The Web container sends events to the server, which then processes and forwards data to other platforms. |
| Data flow | Data goes straight from the browser, easily affected by cookies or ad blockers. | Data passes through the server, offering better control and security. |
| Cross-domain | Each domain works separately and may face cookie limitations. | Both domains must use server-side tagging within the same GTM account for smooth tracking. |
👉 In short: Client-side tagging runs entirely in the browser, while GTM server-side tagging handles data on the server, making it more accurate, secure, and reliable.
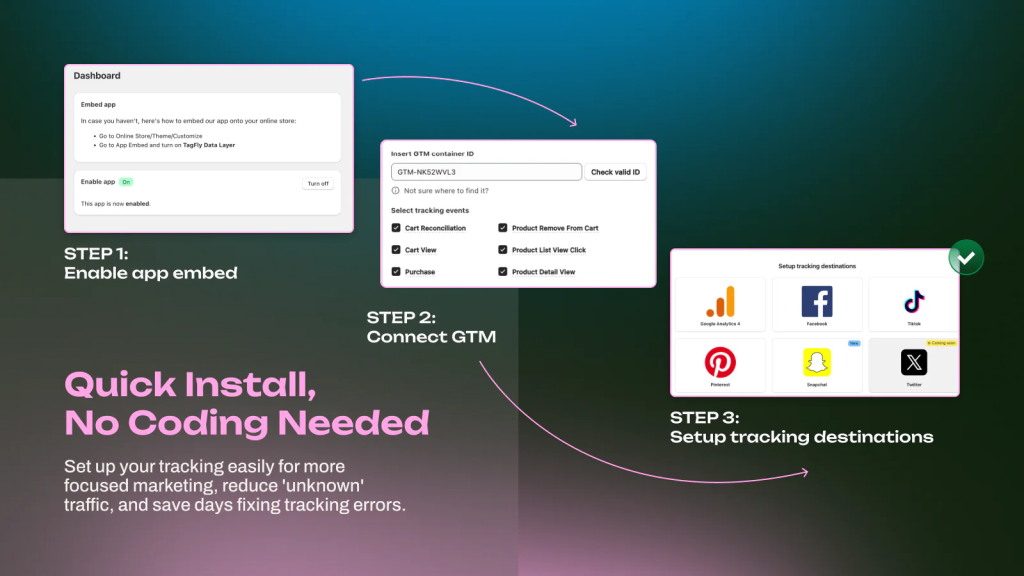
Simplify Server-Side Tracking and Get More Accurate Conversion Data
Setting up server-side tracking doesn’t have to be complex. TagFly Google Ads, Tag Manager makes it simple, fast, and reliable. With ready-to-use GTM containers and Google Tag integration, you can connect GA4, Google Ads, Facebook, TikTok, and Twitter (X) in just minutes.
By sending data through your own server, TagFly ensures higher accuracy, faster performance, and full privacy compliance, so every conversion counts, even when browsers or iOS updates try to block it.
👉 Why marketers love TagFly:
- Accurate, server-verified tracking for all major ad platforms
- Quick setup with prebuilt GTM containers, no coding required
- Works seamlessly with GA4, Google Ads, Facebook, TikTok, and Twitter
- Protects user data and ensures GDPR/CCPA compliance
- Improves site speed by reducing browser load
Conclusion
To sum up, both methods have their place. Client-side tracking is simple and works well for small-scale setups that need quick insights. But as privacy rules tighten and browser restrictions grow, server-side tracking clearly stands out, giving you cleaner data, better control, and long-term stability.
If you’re serious about accuracy and compliance, the winner in the client side vs server side debate is clear: go server-side.