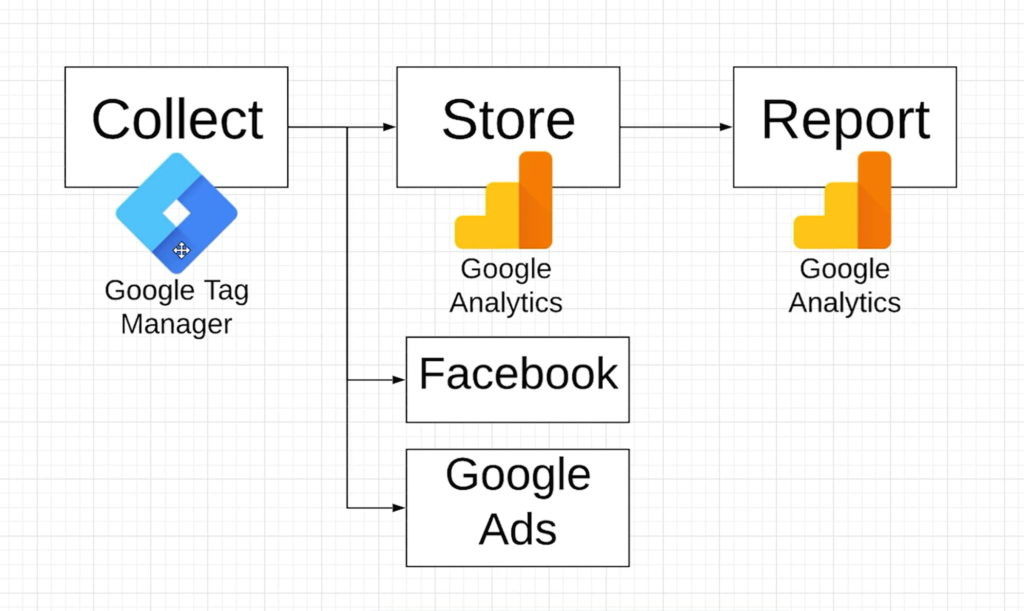
If you’ve read several articles trying to figure out the difference between Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics but are still unsure, this article is intended to be your final stop. Together, we’ll explore the 8 most significant differences and see how these tools work together to enhance your website tracking and analytics. Let’s put an end to the confusion once and for all!
What is Google Tag Manager?
Google Tag Manager is the answer to tracking codes and managing them through an interface on the web or within an app-from user to user-without the need for intervention or modification of tag used by an additional user in the entire process.
Why use Google Tag Manager:
- Making it easier to apply and manage tracking codes.
- Allowing nontechnical users to deploy tags without touching the code of the site.
- Allowing flexibility in tracking custom events such as clicks, form submissions, and video plays.
- Acting as a central platform where all third-party tags like Google Analytics, Facebook Pixel, or conversion tracking tags are managed from one location.
What is Google Analytics?
Google Analytics is a free web analytics tool that provides basic statistics and analysis, enabling web administrators to optimize their business and marketing objectives.
Why use Google Analytics:
- Collecting, storing and analyzing data on usage of the website and app.
- Understanding the behavior of users, like time spent in a session, bounce rates, and paths through the site’s navigation.
- Measuring how well saving conversion goals has performed in marketing campaigns.
- Assessing the demographic characteristics of the audience in order to assist businesses in improving customer experience.
Differences between Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics
Based on my own experience with Google Analytics vs Google Tag Manager, I’ve divided down their individual responsibilities and features to help you understand how they complement one another.
The following are the significant distinctions I’ve noticed, which should clear up any confusion you may have.
1. Purpose
Google Tag Manager is a centralized platform for managing and deploying tracking codes, often known as tags, on websites and applications. Without having to code the website directly, it allows a developer or marketer to set up technologies like Google Ads conversion tags, Facebook Pixel, and custom event tracking.
Thus, dependency on developers is reduced, and the process for tracking is sped up and made efficient.
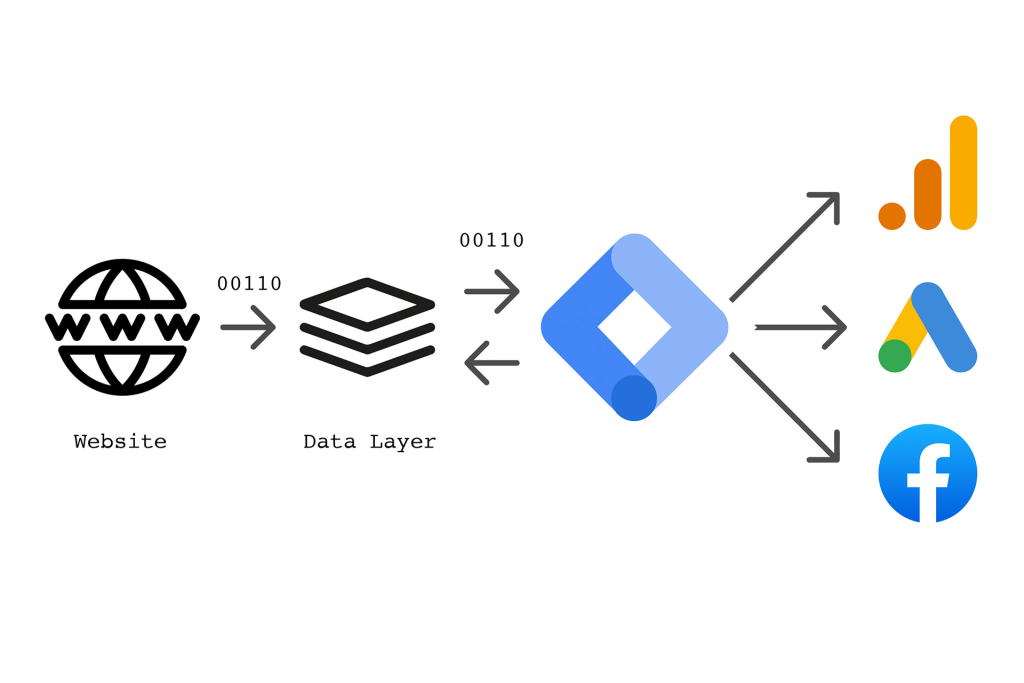
On the contrary, Google Analytics is the one that will interpret the data this way collected from these tags. It is a powerful analytics tool that translates any raw user data into meaningful, insightful information needed for assessing visitor behavior, traffic sources, campaign success, etc.
From tracking audience demographics to identifying high-performing pages and analyzing sales funnels, GA will do it all with actionable intelligence.

Conclusion:
If you’re looking for a solution to efficiently set up and manage tracking tools, Tag Manager is the way to go. However, when your goal is to analyze the results of that tracking to optimize strategies and measure performance, Analytics becomes indispensable.
2. Features
Google Tag Manager simplifies the maintenance of tracking codes, sometimes known as “tags”, on websites and applications, which benefits both developers and marketers. Consider attempting to track every button click, video playback, and form submission on your site.
Without GTM, a developer would have to manually add or change code for each new tag. GTM simplifies this process by allowing you to add and maintain these tags without the need for coding using an intuitive interface. You can also test your tags before they go live and easily resolve mistakes using the debugging and version control features.
Google Analytics, on the other hand, concentrates on analyzing and displaying the data that GTM helps to collect. It has a variety of built-in reports for tracking parameters such as user demographics, session lengths, bounce rates, and traffic sources. Custom dashboard development allows businesses to focus on the KPIs that are most essential to their goals.
GA provides more advanced features than traditional analytics, such as goal monitoring, which measures specific outcomes (such as completed purchases or form submissions), and ecommerce reporting, which provides data on sales, transactions, and product performance.
Conclusion:
Google Analytics excels at comprehending and interpreting the data gathered, even though Tag Manager makes it possible to manage and deploy tracking tools effectively. These products work well together: GA converts tracking configurations into useful information, and GTM provides customizable tracking setups.
3. Event Tracking
GTM is the tool you use to create and define custom events. For example, if you want to know when a user hits a “Sign Up” button, downloads a file, or scrolls to a specific portion of a page, GTM allows you to construct triggers and tags that will fire whenever these events occur. It is especially effective because it removes the need for developers to hard-code these events into your website. GTM allows you to set triggers for actions such as:
- Define triggers for actions like clicks, form submissions, or video plays.
- Configure variables to capture additional details, like the button’s ID or text.
- Send event data to platforms like Google Analytics, Facebook Ads, or TikTok Ads.
GA can track events, although it usually relies on data given via GTM or hard-coded tracking scripts. Events in GA are divided into four categories: Event Category, Event Action, Event Label, and Event Value. These characteristics contribute to the organization and analysis of event data. In GA, you interpret the data acquired by events, such as:
- How many users clicked a specific button.
- Which downloadable files are most popular.
- How users engage with embedded videos.
Conclusion:
GTM simplifies event configuration for recording user interactions on websites and apps, while GA measures and evaluates their impact. Together, they offer a unified system for capturing and evaluating user behaviors.
4. Reporting
Reports are not intended to be provided by Tag Manager. Rather, it serves as a tool for configuring and controlling the tracking tags that transmit information to Facebook Ads Manager and Google Analytics. It is the person that works in the background, making sure that the appropriate data is gathered and routed to the appropriate location.
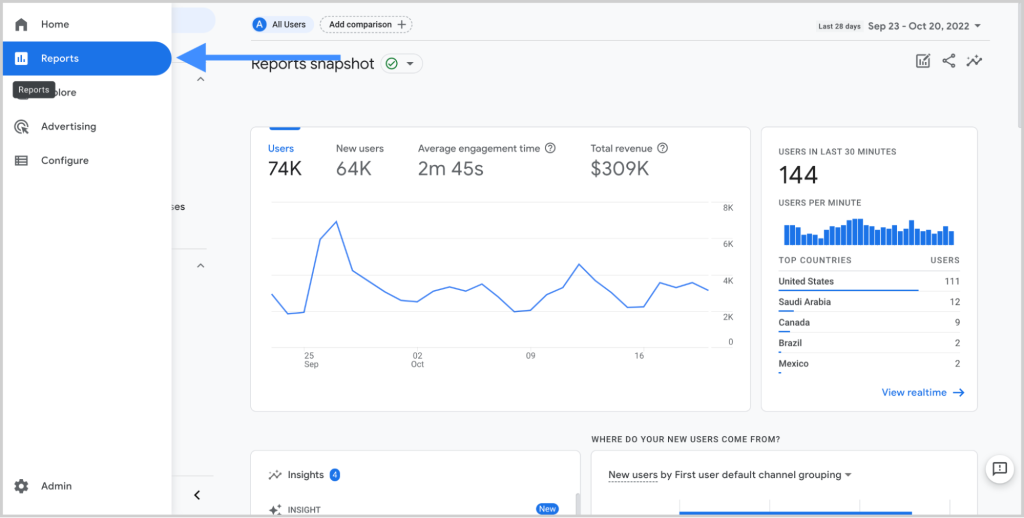
But the main focus of Google Analytics is reporting. GA takes over the task of processing and visualizing the data after the tags are deployed, usually through GTM. You can view what is occurring on your site at any given time with its real-time reporting, including the number of users browsing, the pages they are on, and even their location.
In addition to real-time data, GA provides thorough historical reports that let you monitor patterns over time, examine user behavior, and assess how well your campaigns or web pages are performing.
Conclusion:
GA acts as your spotlight, turning the data into understandable stories about how well your website works. If you want detailed information about how your site is performing and the elements that are influencing its performance, this is the tool you need. The foundation for all those insights is laid by GTM, which ensures that the data is collected accurately.
5. Data querying
Google Analytics is the mainstay when it comes to data querying. It gives users a variety of ways to examine, retrieve, and work with the information gathered from your app or website. To get particular insights about your audience and their activity, you may filter, sort, and segment data using its user-friendly reporting interface. Google Analytics also provides an API for customers who require more customization, allowing companies to link their analytics data with bespoke dashboards or third-party applications like Google Sheets.
However, there is no data querying feature in Google Tag Manager. Deploying and managing the tags that transmit data to advertising tools or platforms like Google Analytics is its responsibility. GTM leaves the analysis and querying to tools like GA after the data is gathered.
Conclusion:
Google Analytics is the best tool to use if you need to examine and evaluate data to find insights that can be put into practice. Through its built-in reports or by connecting to external tools via the API, it provides you with the ability to query and edit your data. Although it is necessary to set up the tracking systems, Google Tag Manager does not offer querying capabilities; instead, it makes sure that the data travels to platforms such as GA, where the actual analysis takes place.
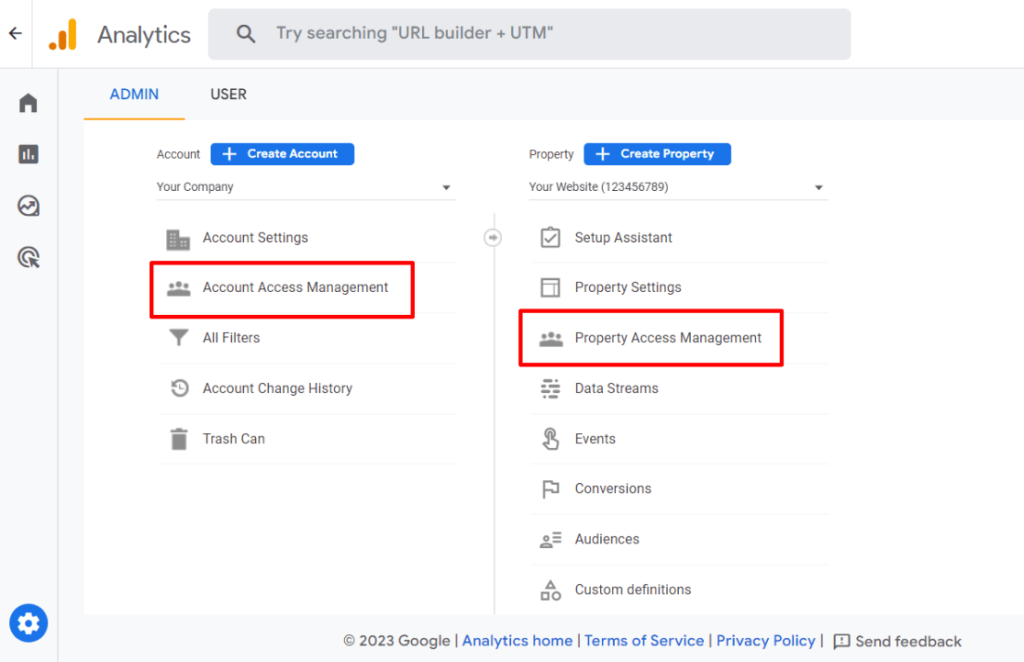
6. User access
The primary function of user access in Google Tag Manager is the deployment and management of tracking tags. It provides fine-grained permission control, which is very helpful for groups where several individuals are in charge of overseeing tracking configurations.
In contrast, Google Analytics concentrates on managing reports and facilitating data access. It enables companies to manage account settings and integrations, as well as who can read, change, and share reports.
Conclusion:
If you’re working with a team, GTM’s permissions help ensure tracking consistency, while GA’s access controls protect your valuable data and insights.
7. Data privacy
No personal information is gathered or processed by Google Tag Manager alone. By adding tags to other platforms that might gather data, it serves just as a facilitator. For instance, GTM may gather data about user demographics or behavior if you use it to add a Google Ads conversion tag or a Facebook Pixel. Although GTM is still privacy-neutral, it is your duty to make sure the tags you use abide by local laws or data privacy standards like the CCPA or GDPR. When using GTM, it is crucial to set up consent banners and tag-triggering rules correctly to prevent unwanted data collection.
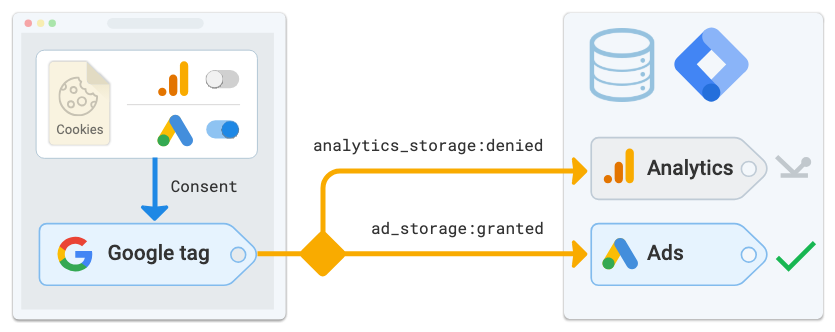
On the other hand, Google Analytics is a data collecting tool that collects and analyzes user data directly, including session data, IP addresses, and behavioral interactions. Businesses using GA are required to take proactive measures to adhere to privacy rules because it handles personal data.
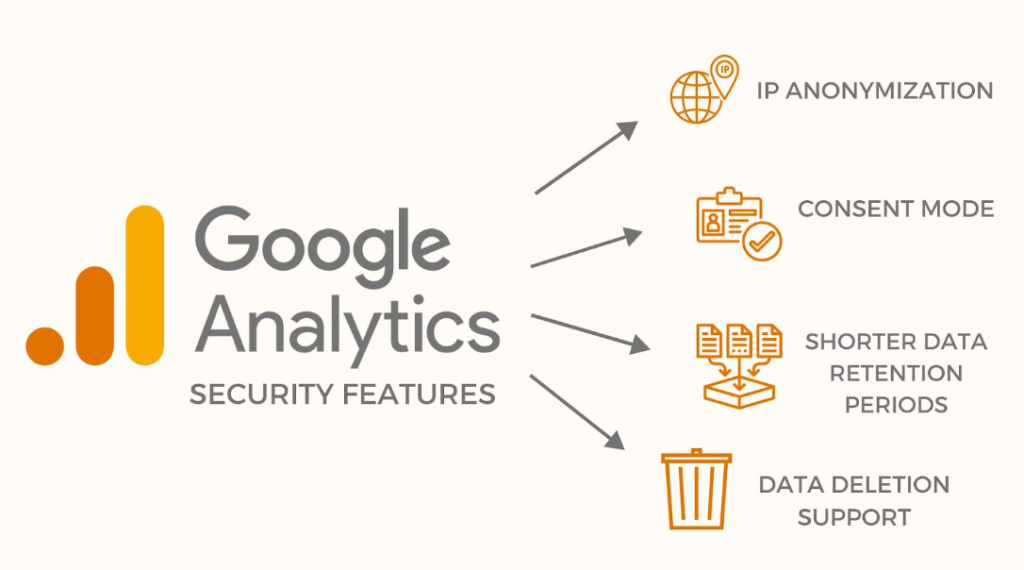
In order to better comply with international privacy requirements, Google Analytics’ most recent version, GA4, has included features including event-based tracking and more controls. Businesses must still be accountable for the way they gather, store, and handle user data, though.
Conclusion:
While GTM sets the foundation, GA must be handled with care to ensure all data is collected and processed transparently and legally.
8. Integration
Google Tag Manager serves as a centralized platform for deploying and managing numerous integrations. It integrates smoothly with third-party platforms, such as
- Advertising tools: Facebook Ads, TikTok Ads,…
- Analytics platforms: Google Analytics, Hotjar,…
- Marketing automation tools: HubSpot or Mailchimp,…
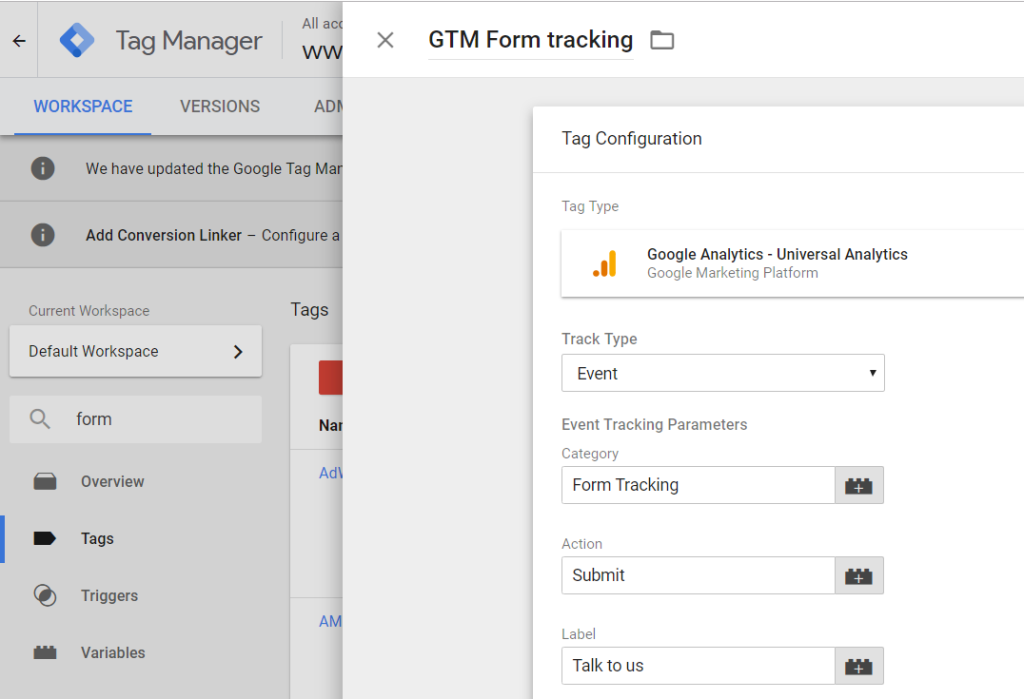
GTM allows you to deploy and manage tags for all of these platforms without modifying your website’s code. For example, GTM enables you to quickly and efficiently install a Facebook Pixel to track ad performance or a TikTok tracking tag to measure conversions. It also supports custom HTML and JavaScript elements, making it extremely adaptable to different tracking needs.
Google Analytics, while focused on analyzing data, integrates deeply within the Google ecosystem:
- Google Ads: Measure the performance of your paid campaigns and link cost data directly to your Analytics reports.
- Google Search Console: Gain SEO insights by understanding how your site performs in organic search and which keywords drive traffic.
- Google Data Studio: Create advanced visualizations and dashboards using your GA data.
GA can also be integrated directly into your website by integrating the tracking code in the HTML or deploying it through GTM. The latter is frequently favored since it simplifies future upgrades and provides greater flexibility over tracking configurations.
Conclusion:
Google Tag Manager offers flexibility and efficiency for maintaining and implementing integrations across many platforms. Google Analytics, on the other hand, shines when linked with the Google ecosystem, providing strong data analysis and visualization tools.
Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics: Which to Choose?
By now, you’ve probably grasped the fundamental differences in the purposes of Google Analytics, and Google Tag Manager. To summarize, here’s a simple breakdown:
- Google Tag Manager: Aids in establishing tracking tags (e.g. Facebook Pixels, Google Tracking Tags) to run advertisements on various sites including Facebook and Google.
- Google Analytics: Helps in viewing reports and analyzing detailed information about the clients visiting the website (i.e. the geolocation where the most traffic originates from, number of visitors, age, gender, etc.)
So, if your goal is to analyze data, go with Google Analytics. If your goal is to implement tracking mechanisms for marketing campaigns, choose Google Tag Manager.
Tagfly Expert Recommendation:
For the best results, our experts at Tagfly recommend using both tools together. Use Google Analytics as a tag in Google Tag Manager to track your website’s key metrics like page views, user behavior, and conversions on your website. For example, you can track how many users complete a purchase or sign up for a newsletter.
Wrap up
Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics aren’t interchangeable, but rather complementing tools. GTM streamlines the deployment and management of tracking codes, whereas GA analyzes the data collected by those codes to deliver actionable insights. GTM makes it simple to add Google Analytics tracking to your website, configure custom event tracking, and determine when specific tags should fire.
I hope this Google Tag Manager vs Google Analytics comparison has helped you understand each tool’s specific roles and how they might operate together to support your company objectives.